- Recommended name
- Goniodomin A seco acid
- Synonyms
- Goniodomin-A seco acid
- Recommended acronym
- GDA-sa
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
No progenitors registered
Vector Species
No vector species registered
- Structure
-
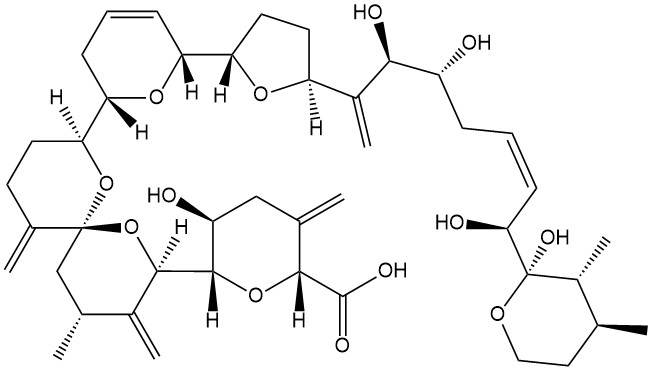
- Formula
- C43H60O12
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 768.41
- Molfile
- see other chem files
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- C=C([C@@]([C@@]5([H])O[C@](C(O)=O)([H])C(C[C@@H]5O)=C)([H])O2)[C@H](C)C[C@@]12O[C@@]([C@@]3([H])O[C@]([C@@]4([H])O[C@@](C([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)C\C=C/[C@H](O)[C@]6(O)OCC[C@H](C)[C@H]6C)=C)([H])CC4)([H])C=CC3)([H])CCC1=C.[*].[B].[C].[2H].[F]
- Alternative SMILES
- n/a
- InChi key
- JSHIQCMMWBSBIH-QKVMJORQSA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C43H62O13/c1-22-18-19-51-43(50,28(22)7)36(46)13-8-10-29(44)37(47)27(6)31-16-17-34(52-31)32-11-9-12-33(53-32)35-15-14-25(4)42(55-35)21-24(3)26(5)39(56-42)40-30(45)20-23(2)38(54-40)41(48)49/h8-9,11,13,22,24,28-40,44-47,50H,2,4-6,10,12,14-21H2,1,3,7H3,(H,48,49)/b13-8-/t22-,24+,28+,29+,30-,31-,32+,33-,34-,35-,36-,37+,38+,39+,40-,42-,43+/m0/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- True
- Chem files
- chemfiles/Goniodomin-A-sa.cdx chemfiles/Goniodomin_A_sa_ohne_Sterochemie.mol
References
- Harris et al., 2024
- Harris, C. M., B. Krock and T. M. Harris (2024). "Goniodomic Acid, a Transient Oxirane Intermediate in the Conversion of the Macrolide Algal Toxin Goniodomin A to Seco Acids." Chemical Research in Toxicology.
- Certified
- False
- Certified links
-
-
n/a
- Non certified reference material
- False
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
References
- Harris et al., 2023
- Transformation of GDA into GDB, GDC and corresponding seco acids highly depends on pH of the mobile stationary phase and the adduct ion (ammonium vs. sodium). Most unaltered GD profiles are obtained by alkaline mobile phases and ammonium adducts.
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- n/a
- Risk assessment
- Unknown
- Molecular targets known
- Unknown
- Molecular targets
- n/a
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- Unknown
- TEF available
- False
- Notes